What is User Experience Design (UX)?
User experience (UX) design is the process by which design teams create products that provide users with meaningful and relevant experiences. This includes the design of the entire acquisition and integration process, including branding, design, usability, and function.
What UX designers do is permanent:
Aside from UI Design, the term “User Experience Design” is frequently used interchangeably with terms like “User Interface Design” and “Usability.” While usability and user interface (UI) design are important aspects of UX design, they are subsets of it; UX design encompasses a wide range of other areas as well. A UX designer is concerned with the entire product acquisition and integration process, including branding, design, usability, and function. It is a story that begins before the user even holds the device.
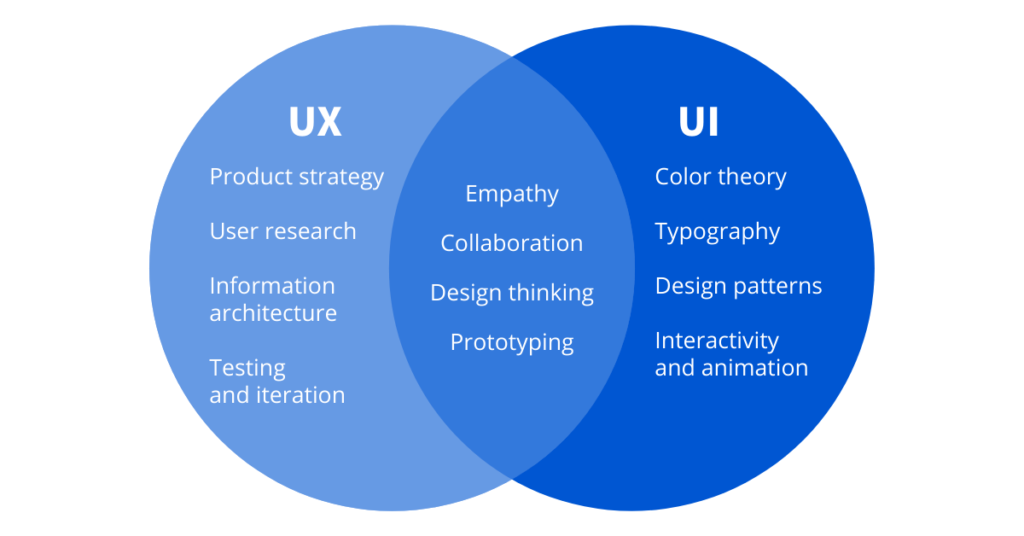
The difference between UI and UX design:
Image Credits: Coursera
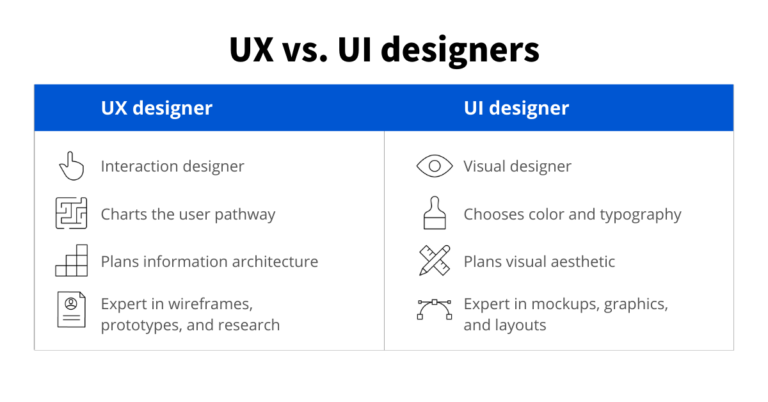
Skill sets of a UI UX designer:
Some skills are shared by UI and UX designers, but each role requires its own set of skills.
Image Credits: Coursera
Ten Things You Should Know About UX and UI Design
The design process is a long and difficult journey that does not happen overnight. It becomes even more complicated if you don’t understand the fundamentals. To help you out, we’ve compiled a list of six things you should know about UX and UI design.
- UX and UI are not the same things:
It is common to confuse the terms “User Experience” (UX) and “User Interface” (UI). It is, however, critical to distinguish between the two. Some may be surprised to learn that UI is a component of UX.
Essentially, user experience design focuses on the product or functionality, the service’s usability, simplicity, and clarity. In short, whether or not users can solve a specific problem within the design and how easy or difficult it is. The visual experience of the product or service, on the other hand, is referred to as the user interface. It is concerned with the appearance and feel of the product/service.
2. You are not the targeted demographic:
Designers, entrepreneurs, and innovators frequently assume that potential customers are similar to them. That is a huge error. A “false-consensus effect” is the psychological term for this tendency. People basically assume that others share their beliefs and will behave similarly to them in a given context. Avoid doing so; many others have done so before you, and it did not end well for them. Whatever product you create, there is a good chance that future users will not be like you. They most likely come from different backgrounds and have different mindsets, mental models, and goals.
- User experience should be viewed as a mindset rather than a procedure:
The wheels must continue to turn, and you must meet a deadline. This is a common reason why UX is not favored. It’s also a common way to determine whether your company truly understands what UX is. User experience design is a mindset, not a process that your team must follow. When designing and developing your product, keep a superior user experience in mind at all times. As a result, it is best to seek the advice of an experienced UI/UX design firm.
- All pages must be reachable with no more than three clicks:
That is only partially correct. The notion that every remote corner of your product should be accessible with a few clicks is simply incorrect. Not every piece of information available should be the first thing users see. The “about company” button is a great example. Those who are interested in the company’s history can delve into it and dig around. In a world where humans have a record low attention span, you must devote all of your attention to what adds value to your users’ lives, the vital information.
- Design for short attention spans should be modified:
Speaking of attention spans, you must be concise when serving your users; avoid overloading them with information. The amount of time someone can focus on a task without being distracted is referred to as their attention span. According to a study conducted by Microsoft in 2015, the average human attention span has decreased from 12 seconds to 8 seconds. That’s terrifying; we have a shorter attention span than a goldfish. A goldfish, to be exact. So, when creating a product, ask yourself, “Would a goldfish be able to use this?” Otherwise, it’s back to the drawing board.
- When designing, use real content:
When demonstrating a new design, avoid using Lorem Ipsum and dummy placeholders everywhere. It’s difficult to find a product that isn’t built around original content, whether it’s text, images, or videos. It’s not a stretch to say that design improves the content. However, many designers make the mistake of plastering lorem ipsum all over their designs, failing to consider content during the design phase.
- Simplicity is a necessity:
The king is simplicity, and the queen is consistency. In the context of digital products, simplicity means that your product is simple to understand and interact with. Your users should not have to read instructions to figure out how to use your product. Your users should not need to read instructions or a sitemap to understand how to use the app. It is your responsibility to make things clear and guide them from where they are to where they need to go.
- Prototype:
Nothing is worse than a design phase that is buried in the basement, never to be seen again until the big curtain reveal. For digital products, the design phase should include a prototyping stage in which users test the product. Usually, a lot of effort is put into creating something that we think is fantastic. As a result, the longer you wait to put this greatness to the test, the more It is stressful to discover that the solution does not work as expected once users get their hands on it.
Prototyping allows you to test your hypothesis before committing to working with an engineering or development team to build the final product. Designers can use a variety of design techniques to accomplish this. Rapid prototyping is a useful technique. It’s a popular method for rapidly developing and validating the future state of a product, whether it’s a website or an app.
THE BOTTOM LINE:
UX design is a multidisciplinary field because it encompasses the entire user journey—UX designers come from a variety of backgrounds including visual design, programming, psychology, and interaction design. Designing for human users entails working with a broader scope in terms of accessibility and accommodating many potential users’ physical limitations, such as reading small text. User research, creating personas, designing wireframes and interactive prototypes, and testing designs are common tasks for a UX designer. These tasks can vary greatly between organizations, but they all require designers to be the users’ advocates and to keep the users’ needs at the forefront of all design and development efforts.
Keeping every such detail in mind and much more, we have the experience of creating the best UI/ UX in design interface, so hire us for your next UI/ UX designing project for having the experience of expert designer services.